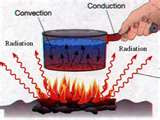
Sunday, July 5, 2009
Saturday, July 4, 2009
Experiments
• A piece of ice is placed in a boiling tube full of water, weighted down by a marble. When top of the tube is heated, the ice doesn't melt as convection currents carry heat upwards.


• Rod, wood in the middle and metal at both corners. However, only the paper at the wood portion scorched.
Reason: METAL IS A GD CONDUCTOR OF HEAT.
• Put a paper cup over the Bunsen burner / flame-----notice the paper cup would burn within a few seconds, however if you put water into the cup, and put over the flame, the paper cup would not burn, instead, the water inside would boil. But why water not the paper cup? The paper is thin and therefore heat is conducted quickly to the water in the paper cup.

• The tiled floor and the woolen rag , even though, they are of the same temperature, the tiled floor feels cold, while the woolen rag is warm, its because, the tile is a better thermal conductor than the woolen rag, thus, it conducted heat at a much rapid rate. That’s the reason why you would turn your feet to the side, so that there is lesser area of contact, thus less heat energy would be conducted away.


• Meat w/o bone
Meat w bone
Which one would cook faster? Both meat are the same, except that one has bone while the other does not have. Meat with bone would cook faster, as bone is a good thermal conductor. So next time, try cooking your meat with the bone still in place!

• If you were to have to serve your guests with baked potato quickly, put metal spoons/forks through the potato at both sides, you will notice that the potato will bake much faster, because the metal spoon/ fork, conduct the heat away from it quickly, the heat energy is then transferred to the potato, thus the potato bake at a faster rate.



• Rod, wood in the middle and metal at both corners. However, only the paper at the wood portion scorched.
Reason: METAL IS A GD CONDUCTOR OF HEAT.
• Put a paper cup over the Bunsen burner / flame-----notice the paper cup would burn within a few seconds, however if you put water into the cup, and put over the flame, the paper cup would not burn, instead, the water inside would boil. But why water not the paper cup? The paper is thin and therefore heat is conducted quickly to the water in the paper cup.

• The tiled floor and the woolen rag , even though, they are of the same temperature, the tiled floor feels cold, while the woolen rag is warm, its because, the tile is a better thermal conductor than the woolen rag, thus, it conducted heat at a much rapid rate. That’s the reason why you would turn your feet to the side, so that there is lesser area of contact, thus less heat energy would be conducted away.


• Meat w/o bone
Meat w bone
Which one would cook faster? Both meat are the same, except that one has bone while the other does not have. Meat with bone would cook faster, as bone is a good thermal conductor. So next time, try cooking your meat with the bone still in place!

• If you were to have to serve your guests with baked potato quickly, put metal spoons/forks through the potato at both sides, you will notice that the potato will bake much faster, because the metal spoon/ fork, conduct the heat away from it quickly, the heat energy is then transferred to the potato, thus the potato bake at a faster rate.

Set 2 answers
- You should wear mittens as it is able to trap heat within the fingers and reduce surface area.
- Fur next to the skin.
- Absorb light wave better so that we can see things.
- Ice is not a full solid. Ice upon freezing gives up heat to plants, thus, people can still grow vegetables during winter.
- More blood directed to your face, so that your face can dissipate heat.
- The tile file conducts heat better.
Set 1 answers
- The road is black and rough, while the cement is grey and smooth. Dull black surface absorb heat faster than bright shiny surface. Thus, the snow on the road melt sooner than on the cement.
- The material with higher emissivities glows the brightest.
- If the fireplace pokers are made of copper, we cannot hold on to it, because it is too hot. Copper conducts heat faster than iron.
- One would find it in cold climates. Air is a poor conductor of heat, thus the air-filled tubes are able to trap heat better, especially useful in cold climates.
- Snow insulates the ground and traps the heat within the ground , so that the water pipes would not freeze.
Set 2
- To keep your hands as warm as possible during skiing, should you wear mittens or gloves?(Mittens, except for the thumb, do not have individual finger compartments.)
- Could one keep warmer in winter wearing a fur coat inside-out, with the fur next to the skin?
- Why is the pupil of the eye black?
- Why ice has low thermal conductivity?
- Why do people people become "flushed" when overheated?
- When one steps from a shower on a cold morning, why does the tile floor seem so much colder than air?
Set 1
- The Sun goes down, snow falls on cement playground and on asphalt road. Why does the snow on the road melt sooner than on cement?
- Two different materials at the same temperature have different emissivities. Which one glows the brightest?
- Why are fireplace pokers made of iron and not copper?
- Some animals have hair which is composed of solid tubular strands, while others have hollow, air-filled tubes. Where would one more likely find the animal with hollow air-filled tubes? In cold climates, or warm?
- In Alaska, a lack of snow allowed the ground to freeze down to a depth of about one meter, causing buried water pipes to freeze and burst. Why did a lack of snow lead to this situation?
Thursday, July 2, 2009
Example of Everyday applications with Radiation
1. A fire-fighting suit needs bright and shiny outer layer so that it is slow to absorb heat energy from the fire.
2. During the day, infared radiation from the sun passes through the glass roof of the greenhouse. This warms up the soil and plants in the greenhouse. As the contents in the greenhouse get warm, they start to emit infared radiation. The infared radiation emitted by the contents in the greenhouse is slightly different compared to the infared radiation emitted by the Sun and is unable to pass through the glass roof. Therefore. the infared radiation emitted by the contents in the greenhouse gets trapped. The amount of infared radiation in the greenhouse gets built up over time, thus, causes the temperature in the greenhouse to rise.
2. During the day, infared radiation from the sun passes through the glass roof of the greenhouse. This warms up the soil and plants in the greenhouse. As the contents in the greenhouse get warm, they start to emit infared radiation. The infared radiation emitted by the contents in the greenhouse is slightly different compared to the infared radiation emitted by the Sun and is unable to pass through the glass roof. Therefore. the infared radiation emitted by the contents in the greenhouse gets trapped. The amount of infared radiation in the greenhouse gets built up over time, thus, causes the temperature in the greenhouse to rise.
Example of Everyday applications with Convection
1. Car engines: Cooled by convection currents in the water pipes. Water is a very good substance to carry the unwanted heat away from the engine to the radiator.
2. The sun can cause very large convection currents of air. This flow of air is wind. In daytime, the land has a higher temperature than the sea. The warm air rises over the land and the coolair falls over the sea. So we feel a breeze from the sea.

3. Rising air over the land are convection currents and are used by glider pilots to keep their gliders in the sky.
4. Air conditioners are installed near the ceiling of the room, to allow the setting up of convection currents. The air-conditioner releases cool dry air into the room. As cool air is denser, it sinks. The warm air, being less dense, will rise. The air circulated and the temperature of the air will eventually fall to the desired value.
5.
Inversion layer. Air near ground is more dense than air higher up; no convection currents to lift pollutants.http://www.blogger.com/post-edit.g?blogID=8541793538969815640&postID=8144138354297716640
6.
Hot room air is forced outside, while cooler air replaces it.
2. The sun can cause very large convection currents of air. This flow of air is wind. In daytime, the land has a higher temperature than the sea. The warm air rises over the land and the coolair falls over the sea. So we feel a breeze from the sea.

3. Rising air over the land are convection currents and are used by glider pilots to keep their gliders in the sky.
4. Air conditioners are installed near the ceiling of the room, to allow the setting up of convection currents. The air-conditioner releases cool dry air into the room. As cool air is denser, it sinks. The warm air, being less dense, will rise. The air circulated and the temperature of the air will eventually fall to the desired value.
5.

Inversion layer. Air near ground is more dense than air higher up; no convection currents to lift pollutants.http://www.blogger.com/post-edit.g?blogID=8541793538969815640&postID=8144138354297716640
6.

Hot room air is forced outside, while cooler air replaces it.
Monday, June 15, 2009
Example of Everyday applications with Conduction
Good conductor of heat:
Cooking pans, kettles, heat exchangers
Good insulator of heat:
Handles of appliances and utensils. table mats, woollen clothes, fibre glass
Fibreglass, felt and expandedpolystyrene foam are used for home insulation.It traps large amounts of air.This prevents heat from passing through the ceiling easily.
Why air?Reason: air is a poor conductor of heat.
Cooking pans, kettles, heat exchangers
Good insulator of heat:
Handles of appliances and utensils. table mats, woollen clothes, fibre glass
Fibreglass, felt and expandedpolystyrene foam are used for home insulation.It traps large amounts of air.This prevents heat from passing through the ceiling easily.
Why air?Reason: air is a poor conductor of heat.
Radiation in all matter
All objects and surfaces emit infrared radiation but at different amounts. When a hot object emit radiation to its surroundings, it becomes cooler. The emitted radiation then reaches other objects, and some of the heat is absorbed. This makes the molecules of the other objects to vibrate faster and so they become hotter.
Factors affecting rate of infrared radiation:
1. Colour and texture of the surface
Dull black surface absorb heat faster than bright shiny surface.
2. Surface area
Large surface area will radiate faster than small surface area.
3. Surface temperature
High temperature will radiate faster than low temperature.

Factors affecting rate of infrared radiation:
1. Colour and texture of the surface
Dull black surface absorb heat faster than bright shiny surface.
2. Surface area
Large surface area will radiate faster than small surface area.
3. Surface temperature
High temperature will radiate faster than low temperature.

From the sun to the earth, it is mostly empty space(vacum). Transfer of heat cannot occur via convection nor conduction, which require the movement of molecules from one place to another or the collisions of molecules within the material. Thus, thermal energy from the sun is transferred to us through radiation which do not require a medium.


Convection in Liquids and Gases
The movement of the liquid due to a difference in its density sets up a convection current.
When a beaker of water is heated under a hot bunsen burner, the water at the bottom of the beaker gets heated up and expands. It is now less dense than the the surrounding water and therefore rises to the top, and bring thermal energy upwards. The surrounding water in the upper part of the flask, being denser, will sink to replace the less dense water. This movement sets up a convection current in the beaker of water.

To see the convection current, place some potassium permanganate crystals at the bottom of the beaker, and one would be able to see the circulation of the purple streams of water.
Convection currents occur only in fluids such as liquids and gases but not solids, because convection involves the bulk movement of the fluids which can carry thermal energy with them. The particles of solids are strongly bonded together and not allowed to flow, thus, solids transfer thermal energy through vibrations, without any bulk movement of the particles themselves.
When a beaker of water is heated under a hot bunsen burner, the water at the bottom of the beaker gets heated up and expands. It is now less dense than the the surrounding water and therefore rises to the top, and bring thermal energy upwards. The surrounding water in the upper part of the flask, being denser, will sink to replace the less dense water. This movement sets up a convection current in the beaker of water.

To see the convection current, place some potassium permanganate crystals at the bottom of the beaker, and one would be able to see the circulation of the purple streams of water.
Convection currents occur only in fluids such as liquids and gases but not solids, because convection involves the bulk movement of the fluids which can carry thermal energy with them. The particles of solids are strongly bonded together and not allowed to flow, thus, solids transfer thermal energy through vibrations, without any bulk movement of the particles themselves.
Conduction in Liquids and Gases
The particles in liquids and gases are spaced further apart than those in solids. Therefore, collisions between molecules are less frequent, thus the process of conduction in liquids and gases is inefficient.
This also explains why air is a poor conductor of heat as compared to water, which in turn is a poor conductor of heat compared to most solids.
Most liquids are poor conductors of heat except molten mercury.
This also explains why air is a poor conductor of heat as compared to water, which in turn is a poor conductor of heat compared to most solids.
Most liquids are poor conductors of heat except molten mercury.
Conduction in Solids--way1
When one end of an object is supplied with thermal energy, the molecules gain kinetic energy and vibrate vigorously. As they vibrate faster, they will collide with neighbouring particles making them vibrate too. Due to the transfer of kinetic energy, the less energetic molecules would vibrate faster and collide with other less energetic molecules in the other end.
This continues until heat energy from the hottert part spreads throughout the colder part.
Energy is passed on from one molecule to another without the molecule moving out from their fixed position. Conduction also happens in all matter, as long as there is a medium.
As conduction transfers thermal energy by the vibration of particles, the closer the particles are packed togther, the more quickly it is for the energy to pass from one particle to another via vibration. That is the reason why conduction occurs the fastest in solids, as compared to liquids and gases.

This continues until heat energy from the hottert part spreads throughout the colder part.
Energy is passed on from one molecule to another without the molecule moving out from their fixed position. Conduction also happens in all matter, as long as there is a medium.
As conduction transfers thermal energy by the vibration of particles, the closer the particles are packed togther, the more quickly it is for the energy to pass from one particle to another via vibration. That is the reason why conduction occurs the fastest in solids, as compared to liquids and gases.

Conduction in Solids--way2
Transferring of thermal energy from hot end to cold end by molecular vibration is quite slow. Another much faster mechanism of thermal energy transfer is, free electrons diffusion. Solids can either be metals or non-metals. Solids which are metal have free electrons which are not possessed by non-metals. When thermal energy is supplied, besides the transfer of heat energy through vibrating molecules, these free electrons also gain kinetic energy. These fast moving electrons then diffuse / spread into the cold end of the metal. They collide with the atoms in the cooler parts of the metal and transfer their kinetic energies to them.
A good conductor is a kind of material with more free electrons, because thermal energy can be transferred more quickly. All metals are therefore good conductor.
The rate of heat transfer determines whether an object is a good/ poor conductor.
A good conductor is a kind of material with more free electrons, because thermal energy can be transferred more quickly. All metals are therefore good conductor.
The rate of heat transfer determines whether an object is a good/ poor conductor.
Sunday, June 14, 2009
Question 4
During very cold weather, ice can form on the surface of puddles of water. If the ice layer is found to be thickening at its lower surface, then how is the thermal energy been transferred?
Ans: Convected away from the ice through the water.
Ans: Convected away from the ice through the water.
Question 3
An unlit match is held near to an extremely hot Bunsen flame. Why does the match not get hot enough to light?
Ans: Air is a bad conductor of heat. Thus, there is not enough heat being transferred from the Bunsen burner to the unlit match.
Wrong Assumptions:
1. The flame is not hot enough.
2. The flame does not radiate any heat sideways.
3. A match can only be lit by striking it on a rough surface.
Ans: Air is a bad conductor of heat. Thus, there is not enough heat being transferred from the Bunsen burner to the unlit match.
Wrong Assumptions:
1. The flame is not hot enough.
2. The flame does not radiate any heat sideways.
3. A match can only be lit by striking it on a rough surface.
Question 2
Which of the following is true?
1. Dog drools(salivates) to allow heat loss by evaporation.
2. Elephant sprays water over its body to allow heat loss by evaporation.
3. Jack rabbit has enormous ears with many blood vessels to dissipate thermal energy faster.
4. Camel has big humps to store water so that it can dissipate thermal energy by convection.
Ans: 1, 2, 3 are correct.
1. Dog drools(salivates) to allow heat loss by evaporation.
2. Elephant sprays water over its body to allow heat loss by evaporation.
3. Jack rabbit has enormous ears with many blood vessels to dissipate thermal energy faster.
4. Camel has big humps to store water so that it can dissipate thermal energy by convection.
Ans: 1, 2, 3 are correct.
Question 1
Some steamboat restaurants use paper pots for their customers to boil the food themselves.
What is the reason for the paper not to catch fire when in contact with the flame?
Ans:
The paper is thin and therefore heat is conducted quickly to the water in the paper pot.
The burning temperature of the paper is higher than the boiling point of water.
What is the reason for the paper not to catch fire when in contact with the flame?
Ans:
The paper is thin and therefore heat is conducted quickly to the water in the paper pot.
The burning temperature of the paper is higher than the boiling point of water.
Radiation
Radiation
Definition: Continual emission of infrared waves from the surface of all bodies, transmitted without the aid of a medium.
In other words, heat energy is transmitted from a hot object to another in the form of infra-red.
As this process of thermal energy transfer do not require medium, thus it can also take place in vacum. That is the reason why Earth is able to receive the thermal energy from the sun.
The electromagnetic waves emitted by the Sun makes us feel warm. Thermal energy from infrared waves is called radiant heat.
Radiation can be transmitted through solids, liquids and gases.
The higher the temperature of the heat source, the higher the frequency of the infra-red radiation it will transmit. High frequency radiation is more penetrating than the low frequency infra-red radiation.
Frequency=the number of times a wave repeats itself in a given time.
In other words, heat energy is transmitted from a hot object to another in the form of infra-red.
As this process of thermal energy transfer do not require medium, thus it can also take place in vacum. That is the reason why Earth is able to receive the thermal energy from the sun.
The electromagnetic waves emitted by the Sun makes us feel warm. Thermal energy from infrared waves is called radiant heat.
Radiation can be transmitted through solids, liquids and gases.
The higher the temperature of the heat source, the higher the frequency of the infra-red radiation it will transmit. High frequency radiation is more penetrating than the low frequency infra-red radiation.
Frequency=the number of times a wave repeats itself in a given time.
Convection
Convection
Definition: Transfer of thermal energy by means of currents in a fluid.
Fluid=liquids/gases
Heat is transmitted from one place to another by the movement of heated particles of a fluid.
Why is it fluid only?
In liquids and gases, the molecules are free to move about, unlike the molecules in solids which can only vibrate at fixed positions.Convection cannot take place in solid because the particles of solid are strongly bonded together and not allowed to flow.
Rmb: Solids can only transfer heat from one region to another through conduction and radiation due to its kinetic model.
Fluid=liquids/gases
Heat is transmitted from one place to another by the movement of heated particles of a fluid.
Why is it fluid only?
In liquids and gases, the molecules are free to move about, unlike the molecules in solids which can only vibrate at fixed positions.Convection cannot take place in solid because the particles of solid are strongly bonded together and not allowed to flow.
Rmb: Solids can only transfer heat from one region to another through conduction and radiation due to its kinetic model.
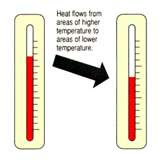
Heat is a type of energy.
Heat energy=Thermal energy
Thermal is the total K.E of the molecules in an object/body. Transfer of thermal energy takes place when there is a difference in temperature, from a higher temperature region to a lower temperature region.
A=50°C B=10°C
When bodies A and B are in contact. A, with a higher temperature than B, would lose heat at a rate faster than the rate at which it absorbs heat from B. While B absorbs heat from A at a rate faster than it loses heat to A. Thus, A loses heat, decrease in temperature, B gains heat, increase in temperature.
Finally, the two bodies would have the same temperature(thermal equilibrium), there is no net flow of thermal energy between them.
Working: (50-10)÷2=20°C
No net flow of thermal energy: 20°C-20°C=0
There are 3 different processes of thermal energy transfer:
1. Conduction, 2. Convection, 3. Radiation

Heat energy=Thermal energy
Thermal is the total K.E of the molecules in an object/body. Transfer of thermal energy takes place when there is a difference in temperature, from a higher temperature region to a lower temperature region.
A=50°C B=10°C
When bodies A and B are in contact. A, with a higher temperature than B, would lose heat at a rate faster than the rate at which it absorbs heat from B. While B absorbs heat from A at a rate faster than it loses heat to A. Thus, A loses heat, decrease in temperature, B gains heat, increase in temperature.
Finally, the two bodies would have the same temperature(thermal equilibrium), there is no net flow of thermal energy between them.
Working: (50-10)÷2=20°C
No net flow of thermal energy: 20°C-20°C=0
There are 3 different processes of thermal energy transfer:
1. Conduction, 2. Convection, 3. Radiation

Conduction
Conduction
Definition: The process of thermal energy transfer without any flow of the material medium.Without any flow of the material medium=Without the medium moving
Heat is transmitted through a medium from its hotter part to its colder part until they are both at the same temperature.
Conduction happens in all matter as long as there is a medium.
The 3 main medium are solids, liquids and gases. Transfer of heat energy is fastest in solids, and slowest in gases.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)